If you’re unfamiliar with the Endocannabinoid system (ECS), you are definitely not alone. In the 1990’s scientists discovered endocannabinoids which are natural cannabis-like molecules produced by the human body to keep the body in homeostasis (equilibrium).
In English?
The endocannabinoid system is a natural collection of endocannabinoids (messenger molecules) and their associated molecules. These endocannabinoids affect your health and mental state by activating specialized message-receivers, called cannabinoid receptors. The endocannabinoid system, with its complex actions in our immune system, nervous system, and all of the body’s organs, acts like a bridge between body and mind. In an article written by MindBodyGreen, according to Martin A. Lee, the director of Project CBD and the author of Smoke Signals, “The endocannabinoid system involves regulating most physiological processes that have been studied: immune function, pain perception, glucose metabolism, blood pressure, bone density, intestinal fortitude, sleep, mood, memory, neuroplasticity, and much more. It’s the reason cannabis and CBD are such versatile medicines that can help so many conditions.
So how exactly does the ECS work?
The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules made by your body. They’re similar to cannabinoids, but they’re produced by your body. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids so far; anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Both of these play a role in keeping internal functions running smoothly. Your body amazingly produces them as needed.
Endocannabinoid Receptors
EDS receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to these receptors in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action (producing Endocannabianoids as needed).
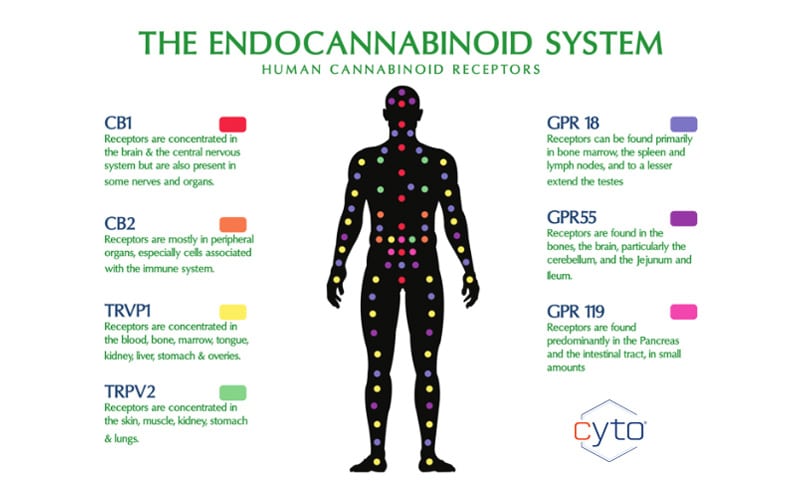
The two main endocannabinoid receptors are CB1 receptors, which are found mostly in the central nervous system and CB2 receptors, which are found mostly in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. However, the resulting effects depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain, while others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation.
Enzymes
Enzymes are responsible for breaking down many things in the body, including endocannabinoids (once they’ve carried out their function). The two main enzymes responsible for this are the fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and the monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG.
The ECS is an extremely complicated system that experts don’t fully understand yet. However, the research is ever evolving and we know enough to understand the basics and how to use our ECS in conjunction with CBD and/or THC to our body’s benefits. Research is showing that ECS’s main function is to keep the body in homeostasis.
Simply put
Simply put in this article: The eCB system is the homeostasis or balancing system for all of our other bodily systems and it is the largest receptor signaling system within the human body. Humans naturally produce endocannabinoids including Anandamide and 2-AG. These endocannabinoids fit like “keys” in the endocannabinoid receptor “lock,” and facilitate systematic balance within our body.